Explore Probiotic rich foods for gut health in summer. Enhance digestion and immunity with yogurt, kefir, kimchi, sauerkraut, kombucha, and miso.
In the quest for better gut health, probiotics have emerged as superheroes, particularly during the summer months. As the temperature rises, our bodies crave lighter, refreshing foods, making it the perfect time to explore the world of probiotic-rich foods.
Understanding Probiotics
What Are Probiotics?
Probiotics are live microorganisms that, when consumed in adequate amounts, offer various health benefits. These microorganisms, typically bacteria or yeast, are naturally present in our bodies, particularly in the digestive system. However, they can also be found in certain foods and supplements.
Probiotics work by promoting a healthy balance of gut bacteria, also known as the microbiome. This balance is crucial for optimal digestion, nutrient absorption, and immune function. Common strains of probiotics include Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, which are often found in fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, and sauerkraut.
How Do Probiotics Benefit Gut Health?
Probiotics play a key role in maintaining gut health through several mechanisms:
Restoring Balance: Factors such as poor diet, stress, and antibiotics can disrupt the balance of gut bacteria, leading to digestive issues and susceptibility to infections. Probiotics help restore this balance by replenishing beneficial bacteria, thereby promoting digestive harmony.
Enhancing Digestion: Certain strains of probiotics produce enzymes that aid in the digestion of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. By improving digestive efficiency, probiotics can alleviate symptoms of bloating, gas, and indigestion.
Read More: What are the 7 stages of vascular dementia? Causes and Risk Factors
Supporting Immunity: A significant portion of the immune system resides in the gut, where probiotics play a vital role in modulating immune function. By stimulating the production of antibodies and enhancing the activity of immune cells, probiotics help defend against harmful pathogens and reduce the risk of infections.
Reducing Inflammation: Imbalances in gut bacteria can contribute to chronic inflammation, which is linked to various health issues, including inflammatory bowel diseases, autoimmune disorders, and obesity. Probiotics exert anti-inflammatory effects by promoting the production of short-chain fatty acids, which help maintain gut barrier integrity and suppress inflammation.
Alleviating Digestive Disorders: Probiotics are beneficial in managing certain digestive disorders, such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and diarrhea. They can help alleviate symptoms such as abdominal pain, diarrhea, and constipation by restoring gut microbial balance and improving bowel function.
Overall, incorporating probiotics into your diet can contribute to better gut health, improved digestion, and enhanced immunity. By nurturing your gut microbiome with these beneficial microorganisms, you can support your overall well-being and enjoy a happier, healthier digestive system.
The Importance of Gut Health
The gut, often referred to as the “second brain,” plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health and well-being. It encompasses the entire digestive system, from the mouth to the anus, and is home to trillions of microorganisms collectively known as the gut microbiome.
Digestion and Nutrient Absorption: One of the primary functions of the gut is to digest food and absorb nutrients essential for the body’s growth, repair, and energy production. Digestive enzymes and acids break down food into smaller molecules, which are then absorbed through the intestinal lining into the bloodstream.
Immune Function: A significant portion of the body’s immune system resides in the gut. The gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT) is a network of immune cells and tissues that helps protect against pathogens and foreign invaders. A healthy gut microbiome is essential for maintaining a balanced immune response and defending against infections.
Synthesis of Vitamins and Hormones: The gut microbiome plays a crucial role in synthesizing certain vitamins, such as vitamin K and some B vitamins, which are essential for various physiological processes, including blood clotting and energy metabolism. Additionally, gut bacteria produce neurotransmitters and hormones that regulate mood, appetite, and stress response.
Gut-Brain Axis: There is a bidirectional communication pathway between the gut and the brain known as the gut-brain axis. This complex network involves neurotransmitters, hormones, and immune signaling molecules that influence mood, cognition, and behavior. A healthy gut microbiome is associated with improved mental health and cognitive function.
Regulation of Metabolism: Emerging research suggests that the gut microbiome plays a role in regulating metabolism and body weight. Imbalances in gut bacteria have been linked to obesity, insulin resistance, and metabolic disorders. By promoting a diverse and balanced microbiome, individuals may support healthy weight management and metabolic function.
Inflammation and Disease Prevention: An imbalance in gut bacteria, known as dysbiosis, can lead to inflammation and contribute to the development of various chronic diseases, including inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), cardiovascular disease, and metabolic syndrome. Maintaining a healthy gut microbiome through diet, lifestyle, and probiotic supplementation may help prevent inflammation and reduce the risk of chronic disease.
In conclusion, gut health is essential for overall health and well-being, influencing digestion, immunity, metabolism, and even mental health. By nurturing a diverse and balanced gut microbiome through a healthy diet, regular exercise, stress management, and probiotic supplementation, individuals can support optimal gut function and promote longevity and vitality.
Top Probiotic Rich Foods for Summer
During the summer months, incorporating probiotic-rich foods into your diet can help support gut health and keep you feeling refreshed. Here are some of the top probiotic-rich foods to enjoy during the summer:
1. Yogurt:
Yogurt is perhaps one of the most well-known probiotic-rich foods. It is made by fermenting milk with beneficial bacteria, such as Lactobacillus bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophilus. These probiotics help promote a healthy balance of gut bacteria and support digestion. Yogurt is versatile and can be enjoyed on its own, mixed with fruit, or used as a creamy topping for dishes.

Table: Nutritional Value of Yogurt
| Nutrient | Amount per 100g |
|---|---|
| Calories | 61 |
| Protein | 3.5g |
| Fat | 3.3g |
| Carbohydrates | 4.7g |
| Calcium | 121mg |
2. Kefir:
Similar to yogurt, kefir is a fermented dairy product made by fermenting milk with kefir grains, which contain a combination of bacteria and yeast. Kefir has a tangy flavor and a thinner consistency than yogurt. It contains a diverse range of probiotic strains, including Lactobacillus acidophilus and Bifidobacterium bifidum. Kefir is rich in protein, calcium, and other nutrients, making it a nutritious addition to smoothies or enjoyed on its own.

Table: Nutritional Value of Kefir
| Nutrient | Amount per 100g |
|---|---|
| Calories | 55 |
| Protein | 3.4g |
| Fat | 3.3g |
| Carbohydrates | 3.9g |
| Calcium | 123mg |
3. Kimchi:
Kimchi is a traditional Korean dish made from fermented vegetables, most commonly cabbage and radishes, seasoned with spices like chili pepper, garlic, and ginger. The fermentation process gives kimchi its tangy flavor and creates a rich source of probiotics, including Lactobacillus kimchii. Kimchi is not only delicious but also packed with vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, making it a popular choice for boosting gut health.
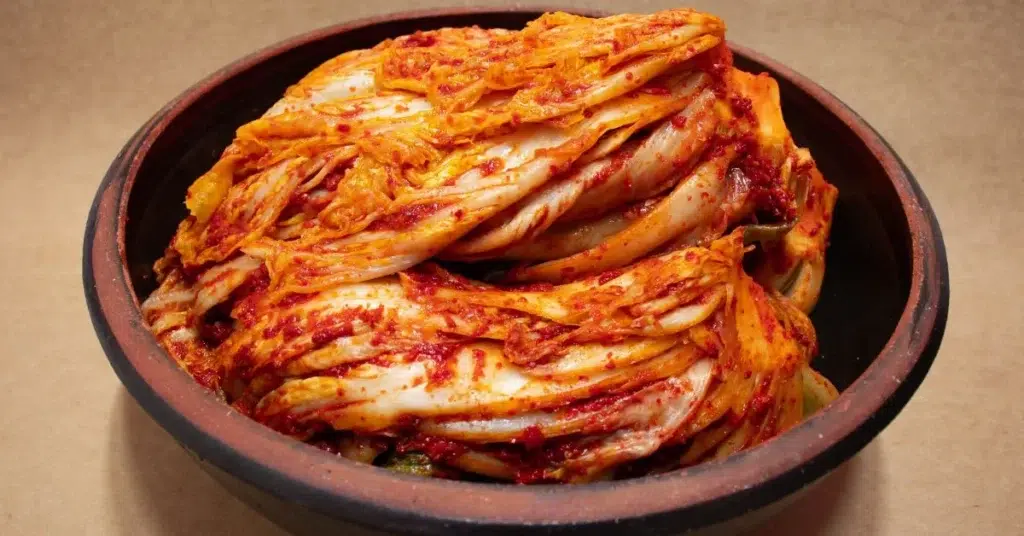

Table: Nutritional Value of Kimchi
| Nutrient | Amount per 100g |
|---|---|
| Calories | 15 |
| Protein | 1.1g |
| Fat | 0.5g |
| Carbohydrates | 2.4g |
| Fiber | 1.8g |
4. Sauerkraut:
Sauerkraut is a type of fermented cabbage that originated in Germany. It is made by lacto-fermentation, where cabbage is salted and left to ferment naturally. During fermentation, beneficial bacteria like Lactobacillus plantarum produce lactic acid, which gives sauerkraut its distinctive sour taste. Sauerkraut is low in calories and rich in fiber, vitamins C and K, and probiotics, making it a nutritious and flavorful addition to salads, sandwiches, or as a side dish.
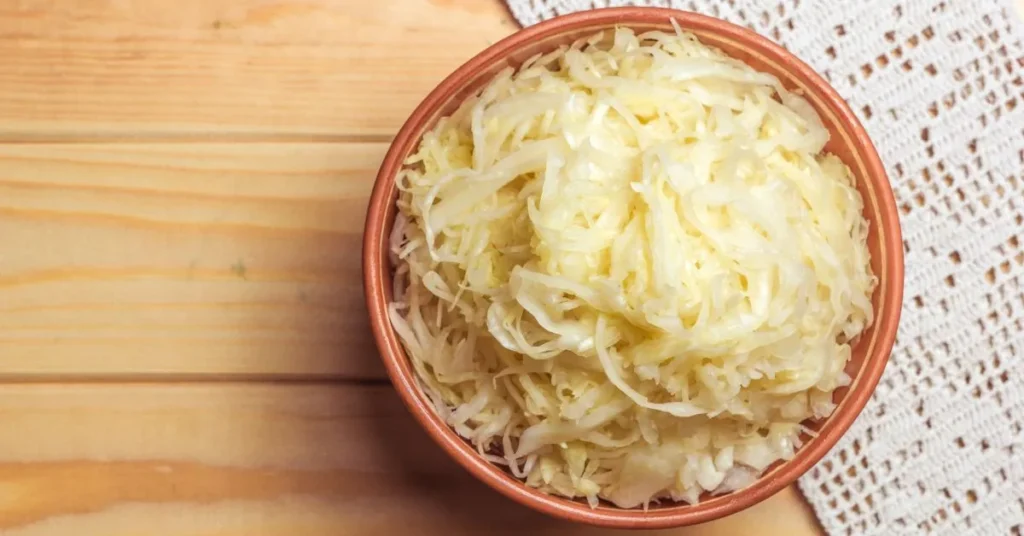

Table: Nutritional Value of Sauerkraut
| Nutrient | Amount per 100g |
|---|---|
| Calories | 19 |
| Protein | 0.9g |
| Fat | 0.1g |
| Carbohydrates | 4.3g |
| Fiber | 2.3g |
5. Kombucha:
Kombucha is a fermented tea beverage that has gained popularity for its tangy flavor and purported health benefits. It is made by fermenting sweetened tea with a symbiotic culture of bacteria and yeast (SCOBY). The fermentation process produces a fizzy drink rich in probiotics, organic acids, and antioxidants. Kombucha comes in a variety of flavors and can be enjoyed as a refreshing alternative to sugary sodas or juices.

Table: Nutritional Value of Kombucha
| Nutrient | Amount per 100g |
|---|---|
| Calories | 16 |
| Protein | 0.4g |
| Fat | 0.0g |
| Carbohydrates | 3.3g |
| Fiber | 0.0g |
6. Miso:
Miso is a traditional Japanese seasoning made by fermenting soybeans with salt and koji (a type of fungus). The fermentation process can vary in length, resulting in different varieties of miso with varying flavors and colors. Miso is rich in probiotics, particularly the strain Bacillus subtilis, and is also a good source of protein, vitamins, and minerals. It is commonly used to flavor soups, marinades, and dressings.
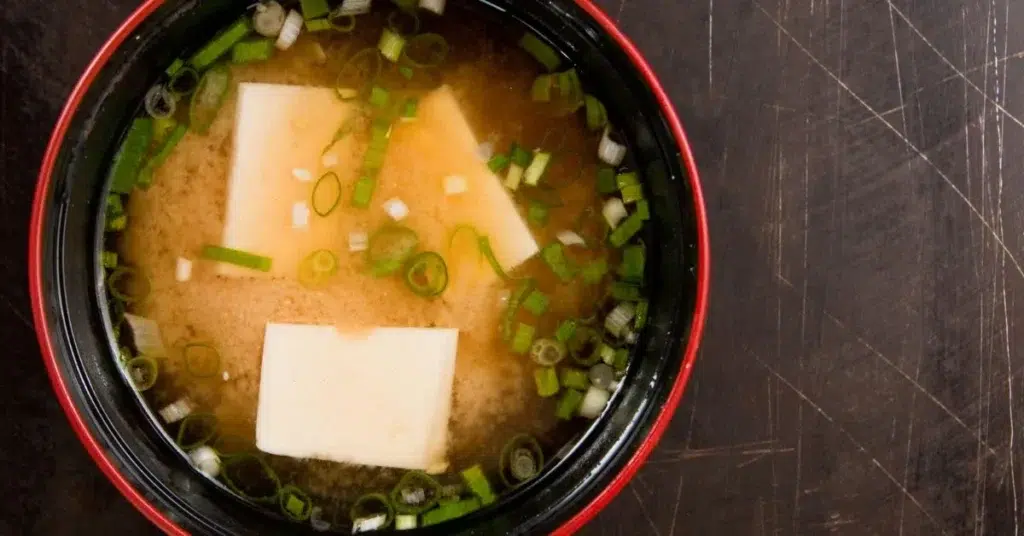

Table: Nutritional Value of Miso
| Nutrient | Amount per 100g |
|---|---|
| Calories | 199 |
| Protein | 12.0g |
| Fat | 6.0g |
| Carbohydrates | 20.0g |
| Sodium | 5172mg |
Incorporating these probiotic-rich foods into your diet during the summer can help support gut health, boost immunity, and promote overall well-being. Enjoy them as part of balanced meals and snacks to reap their delicious and nutritious benefits.
Summer and Gut Health
In summer, we naturally crave lighter foods for easy digestion. Adding probiotic-rich foods like yogurt and kimchi to our diet during this time can enhance gut health. These foods contain beneficial bacteria that aid digestion and support our immune system. By enjoying these refreshing options, we can stay hydrated, nourished, and energized throughout the warmer months. So, as temperatures rise, let’s indulge in these delicious and nutritious treats to keep our gut happy and our bodies feeling refreshed all summer long.
Tips for Maximizing Probiotic Benefits
To get the most out of probiotics, consider these tips:

1. Choose Unpasteurized and Unfiltered Fermented Foods:
Opt for unpasteurized and unfiltered varieties of fermented foods, such as sauerkraut, kimchi, and kombucha. Pasteurization involves heating foods to high temperatures to kill harmful bacteria but can also destroy beneficial probiotics. Choosing unpasteurized options ensures that the probiotic bacteria remain alive and active, maximizing their benefits for gut health.
2. Consume a Variety of Probiotic Strains:
Different probiotic strains offer unique health benefits, so consuming a diverse range of probiotic strains from various sources can help support overall gut health. Look for products that contain multiple strains of probiotics or rotate between different probiotic-rich foods to ensure you’re getting a broad spectrum of beneficial bacteria. This diversity can help optimize the composition of your gut microbiome and enhance its resilience.
By following these tips, you can make the most of probiotics and support a healthy gut microbiome, which is essential for digestive health, immune function, and overall well-being.
Probiotic rich foods for gut health Side Effects and Precautions
While probiotics are generally safe for most individuals, it’s important to be aware of potential side effects and take precautions:
1. Digestive Discomfort:
Some people may experience mild digestive discomfort, such as bloating, gas, or diarrhea, when first introducing probiotics into their diet. This is typically temporary and should resolve as your body adjusts to the new bacteria. Starting with a low dose and gradually increasing intake can help minimize these symptoms.
2. Consultation for Certain Conditions:
If you have a compromised immune system due to conditions like HIV/AIDS or are undergoing medical treatments like chemotherapy, it’s essential to consult with your healthcare provider before adding probiotics to your regimen. Certain strains of probiotics may pose risks for individuals with weakened immune systems, so it’s important to discuss potential benefits and risks with your doctor.
3. Allergic Reactions:
In rare cases, individuals may experience allergic reactions to specific strains of probiotics or ingredients in probiotic supplements. If you have known allergies to dairy, soy, or other common allergens, be sure to check the ingredients list before consuming probiotic products. Discontinue use and seek medical attention if you experience symptoms of an allergic reaction, such as itching, swelling, or difficulty breathing.
4. Risk of Infection:
While probiotics are beneficial for most people, there have been rare reports of probiotic-related infections, particularly in individuals with underlying health conditions or compromised immune systems. These infections are usually associated with strains of probiotics that are not commonly found in foods and supplements. If you experience persistent or severe symptoms after consuming probiotics, seek medical attention promptly.
By being aware of potential side effects and taking appropriate precautions, you can safely incorporate probiotics into your diet and reap their numerous health benefits. If you have any concerns or medical conditions, consult with your healthcare provider before starting a probiotic regimen to ensure it’s safe for you.
Conclusion
Incorporating probiotic-rich foods into your diet is a delicious and convenient way to support gut health, particularly during the summer months when lighter fare is preferred. From creamy yogurt to tangy sauerkraut, there are plenty of options to choose from, each offering its unique blend of beneficial bacteria and nutrients.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ’s)
What foods are good for your gut in the summer?
During summer, incorporate gut-friendly foods like yogurt, kefir, kimchi, sauerkraut, kombucha, and miso into your diet. These probiotic-rich options support digestive health, promote a balanced gut microbiome and help you stay refreshed in the warm weather.
Which food has the highest probiotics?
Foods like kimchi and kefir typically have high levels of probiotics due to their fermentation process, which promotes the growth of beneficial bacteria.
How can I increase probiotics in my gut naturally?
You can naturally increase probiotics in your gut by consuming fermented foods regularly. Incorporate yogurt, kefir, kimchi, sauerkraut, kombucha, and miso into your diet to promote a healthy balance of gut bacteria.
What are 5 probiotic foods?
Five probiotic-rich foods include yogurt, kefir, kimchi, sauerkraut, and miso. Incorporating these foods into your diet can help support a healthy gut microbiome and digestive system.
Which fruit is high in probiotics?
While fruits generally don’t contain high levels of probiotics, some fermented fruits like apples and bananas may contain small amounts of beneficial bacteria. However, for significant probiotic intake, focus on fermented foods like yogurt and kefir.
Are bananas full of probiotics?
Bananas are not rich in probiotics. While they contain some fiber that can support gut health, they don’t naturally contain significant amounts of probiotics. For a higher probiotic intake, consider consuming fermented foods like yogurt or kefir.