Explore effective Parkinson’s Disease Self-Care strategies for optimal symptom management and improved quality of life.
1. What is Parkinson’s disease and the Importance of Parkinson’s disease self-care
Parkinson’s disease is a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by the progressive loss of dopamine-producing cells in the brain. This results in a wide range of symptoms, including tremors, stiffness, impaired balance, and slowness of movement. As the disease advances, individuals may also experience non-motor symptoms such as depression, anxiety, and cognitive changes.

In the management of Parkinson’s disease, self-care plays a pivotal role in promoting overall well-being and quality of life. Parkinson’s disease self-care encompasses a range of strategies aimed at managing symptoms, optimizing treatment outcomes, and fostering independence. From medication management and exercise to nutrition and social support, self-care practices are essential for empowering individuals to take an active role in managing their condition and maintaining a fulfilling lifestyle.
By prioritizing Parkinson’s disease self-care, individuals can better manage their symptoms, improve their overall health, and enhance their quality of life. In this article, we’ll explore the importance of self-care in managing Parkinson’s disease and outline key strategies for optimizing health and well-being.
2. Medication Management For Parkinson’s Disease Patients
Parkinson’s disease self-care encompasses various facets, with medication management standing out as a cornerstone for symptom control and overall well-being. Here’s an overview emphasizing the significance of timely medication intake, structured medication schedules, and addressing medication side effects:

Read More: What are the 7 stages of vascular dementia? Causes and Risk Factors
Timely Medication Intake:
- Adhering to prescribed medication schedules is pivotal in Parkinson’s disease self-care. Consistency in medication intake ensures a steady level of medication in the body, optimizing symptom control throughout the day.
- Timely administration of medications helps minimize fluctuations in symptom severity, promoting stability and enhancing the individual’s quality of life.
- Missing doses or taking medications off-schedule can disrupt symptom management, leading to unpredictable fluctuations and challenges in daily functioning.
Organized Medication Schedules:
- Structuring medication schedules is a proactive approach to Parkinson’s disease self-care. Organizing doses at specific times facilitates adherence and consistency, streamlining the management process.
- Utilizing tools such as pill organizers, medication reminder apps, or setting alarms aids in staying on track with the prescribed regimen, reducing the likelihood of missed doses.
- A well-organized medication schedule serves as a practical framework, empowering individuals to take control of their treatment and optimize symptom management effectively.
Managing Medication Side Effects:
- Addressing medication side effects is integral to Parkinson’s disease self-care. While medications alleviate symptoms, they may also present side effects that impact the individual’s well-being.
- Proactive management of medication side effects involves close communication with healthcare providers. Reporting any adverse reactions promptly allows for timely interventions and adjustments to the treatment plan.
- Exploring strategies to mitigate side effects, such as adjusting dosages, switching medications, or incorporating adjunctive therapies, promotes medication tolerance and enhances overall treatment outcomes.
In essence, Parkinson’s disease self-care revolves around conscientious medication management practices. By prioritizing timely medication intake, implementing organized medication schedules, and effectively addressing medication side effects, individuals can optimize symptom control, improve quality of life, and foster greater independence in daily living.
3. Exercise and Physical Activity for Parkinson’s Disease Patients
Exercise and physical activity play a crucial role in managing Parkinson’s disease symptoms and improving the overall quality of life for patients. Here’s a breakdown of the benefits of exercise, types of exercises recommended, and tips for incorporating daily physical activity routines:
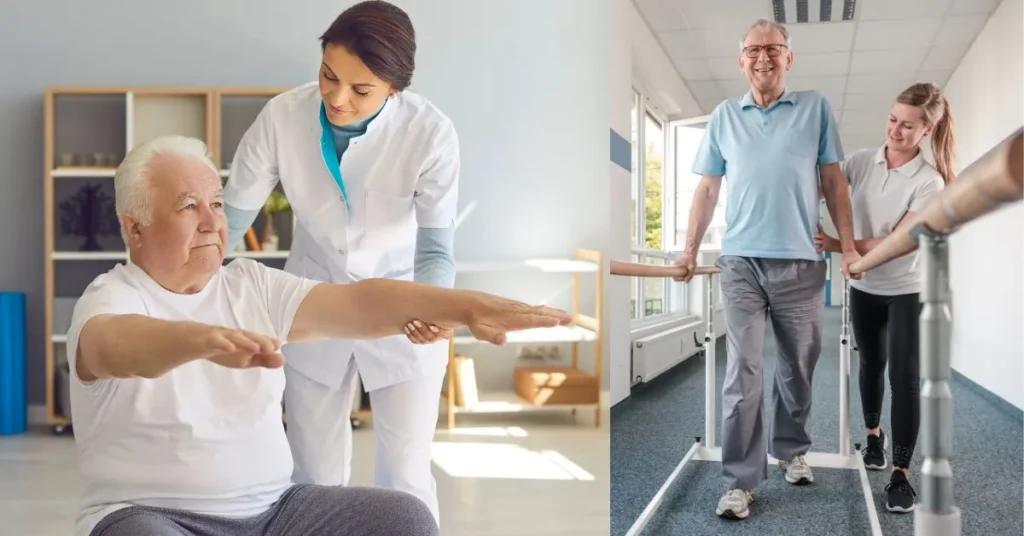

Benefits of Exercise for Parkinson’s Patients:
- Improves Mobility and Balance: Regular exercise helps strengthen muscles, improve flexibility, and enhance balance, reducing the risk of falls and enhancing mobility for Parkinson’s patients.
- Reduces Stiffness and Rigidity: Exercise helps alleviate muscle stiffness and rigidity commonly associated with Parkinson’s disease, promoting a greater range of motion and ease of movement.
- Enhances Mood and Mental Well-being: Physical activity releases endorphins, neurotransmitters that boost mood and alleviate symptoms of depression and anxiety often experienced by Parkinson’s patients.
- Supports Brain Health: Exercise has been shown to promote neuroplasticity, the brain’s ability to adapt and reorganize, potentially slowing the progression of Parkinson’s disease and preserving cognitive function.
- Increases Energy Levels: Engaging in regular physical activity can combat fatigue and increase energy levels, allowing individuals with Parkinson’s to participate more fully in daily activities.
Types of Exercises Recommended:
- Aerobic Exercises: Activities such as walking, cycling, swimming, and dancing are beneficial for improving cardiovascular health, endurance, and overall fitness levels.
- Strength Training: Incorporating resistance exercises using weights, resistance bands, or bodyweight exercises helps build muscle strength, improve posture, and support joint stability.
- Flexibility and Stretching: Stretching exercises improve flexibility, reduce muscle tightness, and enhance range of motion, making daily movements easier and more comfortable.
- Balance and Coordination Exercises: Balance-focused activities, such as tai chi, yoga, or specific balance exercises, help improve balance, coordination, and stability, reducing the risk of falls.
Incorporating Daily Physical Activity Routines:
- Set Realistic Goals: Start with manageable goals and gradually increase the duration and intensity of exercise over time.
- Find Activities You Enjoy: Choose activities that you find enjoyable and engaging to maintain motivation and consistency.
- Schedule Regular Exercise Sessions: Block out dedicated time for exercise in your daily or weekly schedule to prioritize physical activity.
- Mix It Up: Incorporate a variety of exercises to target different muscle groups and prevent boredom. Try alternating between aerobic, strength, flexibility, and balance exercises.
- Listen to Your Body: Pay attention to how your body responds to exercise and adjust intensity or duration as needed. Rest when necessary and avoid pushing yourself too hard.
- Stay Consistent: Aim for regular, consistent exercise to maximize benefits. Even short bouts of activity throughout the day can add up and contribute to overall fitness and well-being.
By incorporating regular exercise and physical activity into daily routines, individuals with Parkinson’s disease can experience significant improvements in mobility, balance, mood, and overall quality of life. Consult with a healthcare professional or physical therapist to develop a personalized exercise plan tailored to your specific needs and abilities.
4. Nutrition and Diet for Parkinson’s Disease Patients
In Parkinson’s Disease Self-Care, Nutrition, and diet play a vital role in managing Parkinson’s disease symptoms and promoting overall health and well-being. Here’s why a balanced diet is important, along with foods to include in the diet and those to avoid or limit:
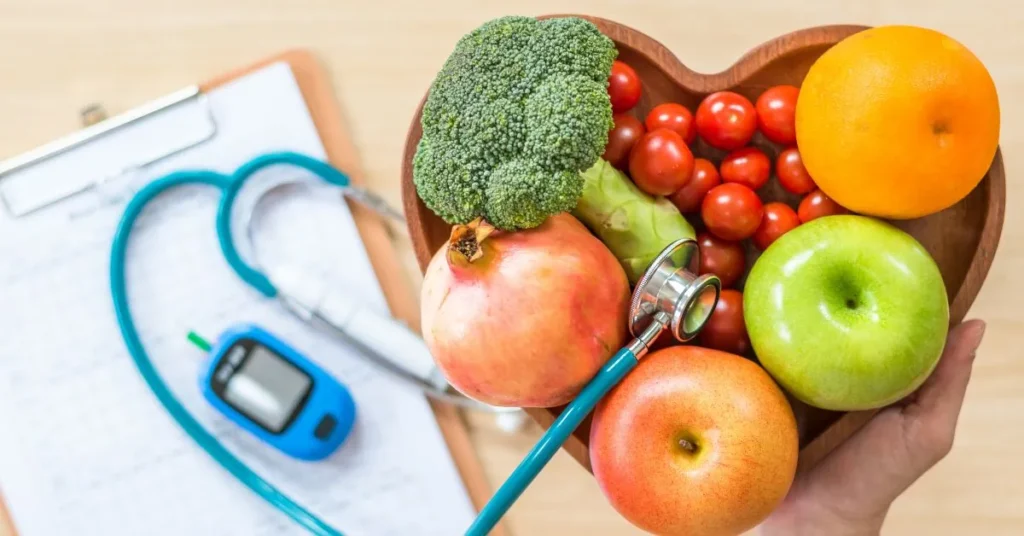

Importance of a Balanced Diet:
- Supports Overall Health: A balanced diet provides essential nutrients, vitamins, and minerals necessary for optimal health, including supporting immune function, maintaining energy levels, and promoting overall well-being.
- Manages Symptoms: Eating a balanced diet can help manage Parkinson’s disease symptoms, such as constipation, fatigue, and muscle stiffness, by providing the body with the nutrients it needs to function properly.
- Supports Medication Efficacy: Certain foods can affect how medications are absorbed and metabolized in the body. Following a balanced diet can optimize medication efficacy and reduce the risk of interactions or side effects.
Foods to Include in the Diet:
- Fruits and Vegetables: Incorporate a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables into your diet to ensure a wide range of nutrients and antioxidants. Aim for at least five servings per day.
- Whole Grains: Choose whole grains such as brown rice, quinoa, oats, and whole wheat bread to provide fiber, vitamins, and minerals while promoting digestive health.
- Lean Proteins: Opt for lean protein sources such as poultry, fish, tofu, beans, and legumes to support muscle health and repair.
- Healthy Fats: Include sources of healthy fats such as olive oil, avocado, nuts, and seeds to support heart health and brain function.
Foods to Avoid or Limit:
- Saturated and Trans Fats: Limit intake of foods high in saturated and trans fats, such as fried foods, fatty meats, processed snacks, and baked goods, as they can contribute to inflammation and cardiovascular disease risk.
- Added Sugars: Minimize consumption of foods and beverages high in added sugars, such as sugary drinks, candies, and desserts, to prevent spikes in blood sugar levels and support overall health.
- Sodium: Reduce sodium intake by choosing low-sodium options and avoiding highly processed foods, canned soups, and packaged snacks high in salt, as excessive sodium intake can contribute to high blood pressure and fluid retention.
- Alcohol and Caffeine: Limit alcohol consumption and monitor caffeine intake, as both can interfere with sleep patterns, exacerbate symptoms such as tremors or dyskinesia, and interact with medications.
By prioritizing a balanced diet rich in nutrient-dense foods and limiting or avoiding processed foods high in unhealthy fats, sugars, and sodium, individuals with Parkinson’s disease can support their overall health, manage symptoms more effectively, and optimize their quality of life. Consulting with a registered dietitian or healthcare provider can provide personalized dietary recommendations tailored to individual needs and preferences.
5. Sleep Hygiene
Sleep hygiene is essential for individuals with Parkinson’s disease to promote restful and rejuvenating sleep, which is crucial for overall health and well-being. Here’s how to address sleep disturbances specific to Parkinson’s, establish a bedtime routine, and create a comfortable sleep environment:
Addressing Sleep Disturbances in Parkinson’s Disease:
- Identify Underlying Causes: Parkinson’s disease can cause various sleep disturbances, including insomnia, restless leg syndrome, sleep apnea, and REM sleep behavior disorder. Identifying and addressing the underlying causes with the help of a healthcare provider is essential.
- Optimize Medication Management: Work with your healthcare provider to adjust Parkinson’s medications or manage side effects that may affect sleep quality. Timing medications appropriately can also help minimize sleep disturbances.
- Address Motor Symptoms: Muscle stiffness, tremors, and other motor symptoms of Parkinson’s can disrupt sleep. Incorporating relaxation techniques, such as gentle stretching or massage, before bedtime may help alleviate these symptoms and promote relaxation.
- Manage Non-Motor Symptoms: Non-motor symptoms like anxiety, depression, and urinary urgency can also impact sleep quality. Addressing these symptoms through medication adjustments, therapy, or lifestyle modifications can improve overall sleep hygiene.
Establishing a Bedtime Routine:
- Set a Consistent Sleep Schedule: Go to bed and wake up at the same time every day, even on weekends, to regulate your body’s internal clock and promote better sleep quality.
- Wind Down Before Bed: Establish a relaxing bedtime routine to signal to your body that it’s time to sleep. This may include activities such as reading, listening to calming music, or practicing relaxation techniques like deep breathing or meditation.
- Limit Stimulants: Avoid stimulants such as caffeine, nicotine, and electronic screens (e.g., smartphones, computers, TVs) before bedtime, as they can interfere with the ability to fall asleep and disrupt sleep patterns.
- Create a Comfortable Sleep Environment: Make your bedroom conducive to sleep by keeping it cool, dark, and quiet. Invest in a comfortable mattress and pillows, and consider using white noise machines or earplugs to block out unwanted noise.
Creating a Comfortable Sleep Environment:
- Manage Light Exposure: Exposure to natural light during the day and minimizing exposure to artificial light, especially blue light emitted by electronic devices, in the evening can help regulate the body’s natural sleep-wake cycle.
- Control Temperature: Keep your bedroom temperature cool and comfortable for sleeping. Consider using fans, air conditioning, or bedding materials that regulate body temperature to prevent overheating or discomfort during the night.
- Reduce Noise and Distractions: Minimize noise and distractions in your bedroom to create a peaceful sleep environment. Use blackout curtains or eye masks to block out light, and consider using white noise machines or earplugs to drown out disruptive sounds.
By addressing sleep disturbances specific to Parkinson’s disease, establishing a consistent bedtime routine, and creating a comfortable sleep environment, individuals can improve sleep quality, enhance overall well-being, and better manage symptoms associated with the condition. If sleep difficulties persist despite these strategies, consulting with a healthcare provider or sleep specialist for further evaluation and treatment options is recommended.
6. Stress Management for Parkinson’s Disease Patients
Stress management is crucial for individuals with Parkinson’s disease as stress can exacerbate symptoms and impact overall well-being. Here’s an overview of the impact of stress on Parkinson’s symptoms, techniques for stress reduction, and mindfulness and relaxation exercises:
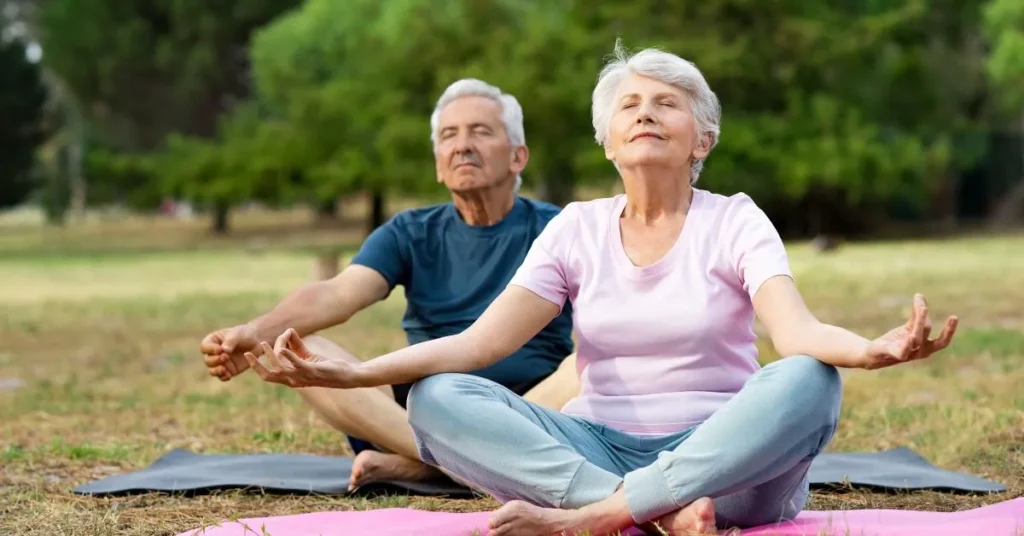

Impact of Stress on Parkinson’s Symptoms:
- Aggravates Motor Symptoms: Stress can worsen motor symptoms such as tremors, rigidity, and bradykinesia (slowness of movement), making them more pronounced and difficult to manage.
- Increases Non-Motor Symptoms: Stress can also contribute to non-motor symptoms such as anxiety, depression, fatigue, and sleep disturbances, further impacting the quality of life for individuals with Parkinson’s.
- Disrupts Medication Efficacy: Stress hormones released in response to stress can interfere with the effectiveness of Parkinson’s medications, leading to fluctuations in symptom control and reduced medication efficacy.
Techniques for Stress Reduction:
- Exercise Regularly: Engaging in regular physical activity, such as walking, cycling, yoga, or tai chi, helps reduce stress levels, improve mood, and promote overall well-being.
- Practice Deep Breathing: Deep breathing exercises, such as diaphragmatic breathing or belly breathing, can activate the body’s relaxation response, reduce stress, and promote a sense of calm.
- Progressive Muscle Relaxation (PMR): PMR involves systematically tensing and relaxing muscle groups throughout the body to release tension, reduce muscle stiffness, and promote relaxation.
- Mindfulness Meditation: Mindfulness meditation involves paying attention to the present moment with openness, curiosity, and acceptance, which can help reduce stress, anxiety, and negative emotions.
- Biofeedback: Biofeedback techniques, such as heart rate variability (HRV) biofeedback or electromyography (EMG) biofeedback, provide real-time feedback on physiological responses to stress, helping individuals learn to control their stress responses effectively.
- Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT is a therapeutic approach that helps individuals identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors contributing to stress, anxiety, and depression.
Mindfulness and Relaxation Exercises for Parkinson’s Disease Patients:
- Body Scan: Body scan meditation involves systematically focusing attention on different parts of the body, noticing sensations without judgment, and promoting relaxation and body awareness.
- Guided Imagery: Guided imagery uses visualization techniques to create calming and relaxing mental images, reducing stress and promoting a sense of peace and well-being.
- Progressive Muscle Relaxation (PMR): As mentioned earlier, PMR involves systematically tensing and relaxing muscle groups to release tension and promote relaxation throughout the body.
- Breath Awareness: Breath awareness meditation focuses on observing the breath without trying to control it, promoting relaxation, reducing stress, and enhancing mindfulness.
- Body-Mind Awareness: Body-mind awareness exercises, such as yoga or tai chi, combine physical movement with mindfulness practices to promote relaxation, stress reduction, and overall well-being.
By incorporating stress management techniques such as regular exercise, deep breathing, mindfulness meditation, and relaxation exercises into daily routines, individuals with Parkinson’s disease can reduce stress levels, improve symptom management, and enhance overall quality of life. Working with healthcare professionals or therapists experienced in stress management can provide additional support and guidance in developing effective stress reduction strategies tailored to individual needs.
7. Social Support for Parkinson’s Disease Patients
Social support is invaluable for individuals living with Parkinson’s disease, providing emotional, practical, and informational assistance that can significantly impact their well-being. Here’s why a strong support system is essential, along with the benefits of joining support groups or online communities, and the importance of communicating needs with friends and family:

Importance of a Strong Support System:
- Emotional Support: Dealing with Parkinson’s disease can be emotionally challenging, and having a strong support system can provide comfort, encouragement, and understanding during difficult times.
- Practical Assistance: Parkinson’s symptoms may impact daily activities, and having a support system in place can help with tasks such as transportation, meal preparation, and household chores, easing the burden on the individual with Parkinson’s.
- Informational Support: Access to reliable information, resources, and guidance from peers, caregivers, and healthcare professionals within a support network can empower individuals with Parkinson’s to make informed decisions about their treatment and self-care.
Joining Support Groups or Online Communities:
- Peer Support: Connecting with others who are experiencing similar challenges through support groups or online communities provides a sense of belonging and validation, reducing feelings of isolation and loneliness.
- Sharing Experiences: Participating in support groups allows individuals to share their experiences, insights, and coping strategies with others, fostering mutual understanding and empathy within the community.
- Access to Information and Resources: Support groups and online communities offer access to valuable information, resources, and educational materials about Parkinson’s disease management, treatment options, and available support services.
Communicating with Friends and Family about Needs:
- Open Communication: Communicating openly with friends and family members about one’s needs, concerns, and challenges related to Parkinson’s disease fosters understanding, empathy, and support within the familial network.
- Expressing Preferences: Clearly expressing preferences, boundaries, and preferences regarding caregiving and support allows friends and family members to assist in ways that are helpful and respectful of the individual’s autonomy and dignity.
- Seeking Help When Needed: Knowing when to ask for help and being comfortable reaching out to friends and family members for assistance with specific tasks or emotional support is essential for maintaining overall well-being and managing Parkinson’s disease effectively.
By cultivating a strong support system, participating in support groups or online communities, and communicating openly with friends and family about needs and challenges, individuals with Parkinson’s disease can enhance their emotional resilience, access valuable resources and information, and feel more empowered in managing their condition and improving their quality of life.
8. Cognitive Stimulation
Cognitive stimulation is crucial for individuals with Parkinson’s disease to maintain cognitive function and overall brain health. Here are some strategies to help individuals with Parkinson’s disease maintain cognitive function, including engaging in brain games and puzzles, as well as continued learning and education:

Strategies to Maintain Cognitive Function:
- Stay Mentally Active: Engage in activities that challenge the brain regularly to maintain cognitive function. This includes activities such as reading, solving puzzles, playing musical instruments, and learning new skills or hobbies.
- Maintain Social Connections: Social interaction stimulates the brain and supports cognitive health. Stay connected with friends, family, and community members through regular social activities, conversations, and group gatherings.
- Manage Stress: Chronic stress can negatively impact cognitive function. Practice stress-reduction techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, yoga, and relaxation exercises to promote cognitive well-being.
- Get Adequate Sleep: Quality sleep is essential for cognitive function and memory consolidation. Establish a regular sleep schedule, create a comfortable sleep environment, and prioritize good sleep hygiene practices.
- Follow a Balanced Diet: Proper nutrition supports brain health. Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats to provide essential nutrients for optimal cognitive function.
- Stay Physically Active: Regular exercise not only benefits physical health but also supports cognitive function. Aim for a combination of aerobic exercise, strength training, and flexibility exercises to promote overall well-being.
Brain Games and Puzzles for Parkinson’s Disease Patients:
- Crossword Puzzles: Solve crossword puzzles to challenge vocabulary, language skills, and memory recall.
- Sudoku: Engage in Sudoku puzzles to improve problem-solving abilities, logical reasoning, and spatial awareness.
- Word Games: Play word games such as Scrabble, Boggle, or word search puzzles to enhance language skills, memory, and cognitive flexibility.
- Brain Training Apps: Use mobile apps or online platforms specifically designed for brain training exercises and cognitive stimulation, such as Lumosity, Elevate, or Peak.
- Board Games: Enjoy board games like chess, Scrabble, or strategic card games to stimulate critical thinking, planning, and decision-making skills.
Continued Learning and Education:
- Take Classes or Workshops: Enroll in classes or workshops on topics of interest to continue learning and expanding knowledge. This could include academic courses, art classes, cooking workshops, or language lessons.
- Read Regularly: Read books, newspapers, magazines, or online articles on a variety of subjects to stimulate cognitive function, expand vocabulary, and keep the mind active.
- Attend Lectures or Seminars: Attend lectures, seminars, or presentations on topics relevant to personal interests or professional development to engage in lifelong learning and intellectual stimulation.
- Online Learning Platforms: Explore online learning platforms such as Coursera, Udemy, or Khan Academy to access a wide range of courses and educational resources from the comfort of home.
By incorporating these strategies into daily routines, individuals with Parkinson’s disease can promote cognitive stimulation, maintain cognitive function, and support overall brain health as they age. It’s important to find activities that are enjoyable and engaging to ensure long-term adherence and benefit.
9. Adaptive Devices and Assistive Technology
Adaptive devices and assistive technology play a significant role in enhancing the daily lives of individuals living with Parkinson’s Disease Self-Care. These tools are designed to aid in various activities, promote mobility, and foster independence. Here’s an overview of the tools available, including assistive devices for mobility and independence, and resources for accessing adaptive technology:

Tools to Aid in Daily Activities:
- Medication Dispensers: Automated medication dispensers can help individuals manage their medications more effectively by organizing and dispensing doses at the appropriate times. This promotes adherence to medication regimens, a crucial aspect of Parkinson’s Disease Self-Care.
- Grip Aids: Grip aids such as adaptive utensils, jar openers, and pen grips can assist individuals with hand tremors or weakness in holding and manipulating objects during daily activities like eating, cooking, and writing.
- Voice-Activated Devices: Voice-activated assistants and smart home devices can be utilized to control lights, appliances, and other electronic devices, minimizing the need for manual dexterity and promoting independence.
- Adaptive Clothing: Clothing designed with adaptive features such as Velcro closures, magnetic buttons, and elastic waistbands can make dressing and undressing easier for individuals with mobility limitations or tremors.
- Personal Emergency Response Systems (PERS): PERS devices, including wearable pendants or wristbands, allow individuals to call for help in case of emergencies, providing peace of mind and reassurance for both the individual and their caregivers.
Assistive Devices for Mobility and Independence:
- Walking Aids: Mobility aids such as canes, walkers, and rollators provide support and stability for individuals with Parkinson’s Disease Self-Care, enabling them to maintain balance and navigate safely during daily activities and outings.
- Wheelchairs and Scooters: Wheelchairs and mobility scooters offer increased mobility and independence for individuals with Parkinson’s Disease Self-Care who may have difficulty walking or standing for extended periods.
- Stairlifts and Ramps: Installing stairlifts or ramps in the home can facilitate safe and accessible movement between different levels, allowing individuals to remain in their homes and navigate stairs with greater ease.
- Bed Rails and Transfer Aids: Bed rails and transfer aids assist individuals with Parkinson’s Disease Self-Care in safely getting in and out of bed, reducing the risk of falls, and promoting independence in daily living activities.
Accessing Resources for Adaptive Technology:
- Occupational Therapy Services: Occupational therapists can assess individual needs and recommend appropriate adaptive devices and assistive technology to enhance independence and quality of life. They can also provide training on device use and adaptation techniques.
- Assistive Technology Centers: Many communities have assistive technology centers or resource centers that offer information, demonstrations, and loan programs for adaptive devices and assistive technology.
- Online Retailers: Online retailers specializing in adaptive devices and assistive technology offer a wide range of products for purchase, with options to suit different needs, preferences, and budgets.
- Nonprofit Organizations: Organizations dedicated to supporting individuals with Parkinson’s Disease Self-Care may offer grants, funding, or assistance programs to help cover the cost of adaptive devices and assistive technology.
By utilizing adaptive devices and assistive technology, individuals with Parkinson’s Disease Self-Care can overcome challenges, maintain independence, and improve their overall quality of life. It’s essential to explore available resources, consult with healthcare professionals, and select devices that best meet individual needs and preferences.
10. Regular Medical Check-ups for Parkinson’s Disease Patients
Regular medical check-ups are essential for individuals with Parkinson’s Disease Self-Care to effectively manage their condition and ensure optimal health outcomes. Here’s why regular visits to healthcare providers are important, including monitoring symptoms and disease progression and discussing treatment adjustments and concerns:

Importance of Regular Visits to Healthcare Providers:
- Early Detection and Intervention: Regular check-ups allow healthcare providers to monitor Parkinson’s symptoms, detect any changes or complications early, and intervene promptly to prevent further progression of the disease.
- Medication Management: Healthcare providers can assess the effectiveness of current medications, adjust dosages prescribe new medications as needed, and address any medication-related side effects or complications.
- Comprehensive Evaluation: Regular visits provide an opportunity for a comprehensive evaluation of physical, cognitive, and emotional health, allowing healthcare providers to address any emerging issues or concerns.
- Coordination of Care: Healthcare providers can coordinate care with other members of the healthcare team, including neurologists, physical therapists, occupational therapists, and speech therapists, to ensure a holistic approach to Parkinson’s Disease Self-Care management.
Monitoring Symptoms and Disease Progression:
- Assessment of Motor Symptoms: Healthcare providers can assess motor symptoms such as tremors, stiffness, bradykinesia (slowness of movement), and postural instability to evaluate disease progression and adjust treatment accordingly.
- Evaluation of Non-Motor Symptoms: Regular check-ups also involve evaluating non-motor symptoms such as depression, anxiety, cognitive changes, sleep disturbances, and autonomic dysfunction, which can significantly impact the quality of life and overall well-being.
- Objective Measures: Healthcare providers may use objective measures such as standardized rating scales and assessments to quantitatively evaluate symptoms and track changes over time, providing valuable insights into disease progression and treatment response.
Discussing Treatment Adjustments and Concerns with Medical Professionals:
- Treatment Optimization: Regular visits provide an opportunity to discuss treatment options, adjust medications or therapies, and optimize Parkinson’s Disease Self-Care management strategies based on individual needs and preferences.
- Addressing Concerns: Healthcare providers can address any concerns or questions regarding treatment, medication side effects, lifestyle modifications, or changes in symptoms, providing guidance, reassurance, and support to individuals and their caregivers.
- Educational Opportunities: Regular check-ups offer educational opportunities for individuals and caregivers to learn more about Parkinson’s Disease Self-Care management, self-care techniques, and available resources and support services.
By prioritizing regular visits to healthcare providers, individuals with Parkinson’s Disease Self-Care can proactively manage their condition, monitor symptoms and disease progression, and collaborate with medical professionals to optimize treatment and support their overall health and well-being. Open communication, active participation in healthcare decisions, and adherence to treatment recommendations are essential for achieving optimal outcomes and maintaining a high quality of life.
11. Conclusion
Parkinson’s disease self-care is multifaceted, involving various strategies to manage symptoms, improve overall well-being, and maintain independence. By implementing the ten self-care practices outlined above, individuals with Parkinson’s disease can optimize their health and quality of life. It’s essential to prioritize self-care, including medication management, exercise, nutrition, and seeking support from healthcare professionals and support networks. With proactive self-care efforts, individuals can navigate the challenges of Parkinson’s disease with resilience and empowerment, enhancing their overall well-being and quality of life.
12. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ’s)
What role does exercise play in managing Parkinson’s disease?
Exercise helps improve mobility, balance, and physical function while also promoting overall health and well-being.
How can I manage medication side effects effectively?
Communicate openly with your healthcare provider about any side effects you experience, and explore potential adjustments to your treatment plan.
Are there specific dietary recommendations for Parkinson’s patients?
A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins is generally recommended. Limiting processed foods and excessive caffeine may also be beneficial.
What are some effective stress management techniques for Parkinson’s patients?
Deep breathing exercises, meditation, yoga, and engaging in enjoyable activities can help reduce stress levels and improve overall well-being.
How can I find support groups or online communities for individuals with Parkinson’s disease?
Your healthcare provider or local Parkinson’s disease organization may be able to provide information on support groups or online communities in your area.


